Published 20:25 IST, July 10th 2024
UniCredit-ECB spat could sharpen watchdog’s teeth
Orcel’s 60 billion euro bank is fighting the ECB, which recently ordered the lender to get out of Russia faster.
- Opinion
- 3 min read

Hypothetically speaking. Andrea Orcel’s last big courtroom battle, over a rescinded CEO job offer from Banco Santander, was a source of entertainment for rival bank executives. Now UniCredit, the lender he runs, has mounted a legal challenge over demands by regulators at the European Central Bank for a quicker exit from Russia. The case could have consequences for the supervisor’s approach to other issues like climate change.
Orcel’s 60 billion euro bank is fighting the ECB, which recently ordered the lender to get out of Russia faster. UniCredit said last week that it had concerns about the terms on which a quicker shrinkage would take place and is asking the General Court of the European Union to opine on whether the ECB’s action has a solid legal basis.
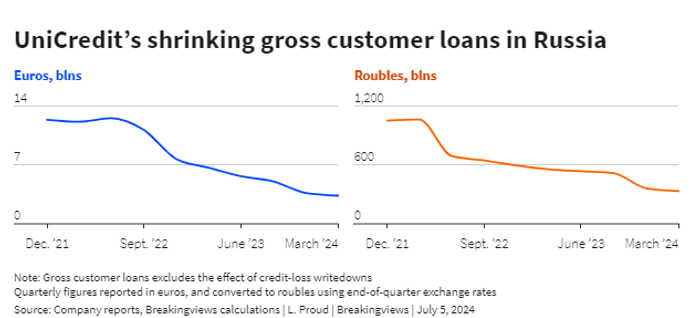
Orcel has already shrunk UniCredit’s Russian gross customer loans by about three-quarters between December 2021 and March 2024 to about 3 billion euros. But the ECB wants him to pick up the pace, fearing a reputational or operational hit if UniCredit stays in the heavily sanctioned country.
Orcel’s bank, according to a person familiar with the case, worries that trying to quit abruptly could anger Russian authorities and lead them to confiscate its assets. That risk is clear and tangible, it will argue, while the ECB’s concerns are hypothetical and unquantifiable, which makes the order disproportionately punitive.
Worryingly for Orcel, European judges have tended to favour the ECB. The regulator has won about 75% of the General Court challenges brought by banks, a person familiar with the process told Breakingviews. If that happens again in the UniCredit case, it ought to grab other lenders’ attention.
The ECB’s main concerns over UniCredit’s Russian business are hypothetical, such as the possibility of Orcel’s bank accidentally processing payments for a sanctioned person. While that risk has not yet materialised, the ECB thinks the danger is acute enough to want UniCredit to radically cut back its business. A similar line of thinking could apply to the watchdog’s green policies: loan losses from climate change haven’t generally happened yet, but the ECB is still considering fines for banks that have been slow to reassess their exposure to polluting companies.
Banks would likely dispute any charges in court, but their cases may be weakened if UniCredit’s action establishes a precedent for the ECB to penalise hypothetical, hard-to-quantify risks. Moreover, a victory against Orcel could even embolden the supervisor to take a tougher stance when handing down fines. Whether they agree with Orcel or not, bank executives have a stake in his case.
Updated 20:25 IST, July 10th 2024